区块链交易zjs
Understanding Blockchain Transaction Status
In the realm of blockchain technology, transaction status refers to the current state or condition of a transaction that has been initiated on a blockchain network. As blockchain serves as a decentralized and distributed ledger, transactions are the fundamental units of activity within this ecosystem. Here, we'll delve into the meaning of different transaction statuses and what they signify in various blockchain networks.
What Does Transaction Status Signify?
1.
Pending
: When a transaction is initiated but has not yet been confirmed by the network, it is said to be in a pending state. During this time, the transaction exists in the network's mempool, waiting to be included in the next block by miners or validators.2.
Confirmed
: Once a transaction is successfully included in a block and added to the blockchain, it achieves the status of being confirmed. Confirmations indicate the number of blocks that have been added on top of the block containing the transaction, providing increasing levels of certainty regarding its validity.3.
Failed
: A transaction may fail to be confirmed due to various reasons, such as insufficient gas fees (in Ethereum) or conflicting transactions. In such cases, the transaction remains pending for a certain period before being dropped from the mempool, returning any funds involved to their original addresses.4.
Reversed or Reverted
: In some blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, transactions can be reversed or reverted due to smart contract conditions not being met or due to errors in the execution of the transaction. This status indicates that the effects of the transaction have been undone, returning the blockchain to its state before the transaction occurred.5.
Stuck or Dropped
: Occasionally, transactions may get stuck in the mempool for an extended period without being confirmed. This could happen due to network congestion or low transaction fees. If a transaction remains stuck for too long, it may eventually be dropped from the mempool, requiring the sender to reinitiate the transaction with higher fees.Implications of Transaction Status
Confirmation Time
: The time taken for a transaction to be confirmed depends on factors like network congestion, transaction fees, and the consensus mechanism of the blockchain network. Users should be aware of potential delays during periods of high network activity.
Security and Finality
: Confirmations provide increasing levels of security and finality to transactions. The more confirmations a transaction has, the more difficult it becomes to reverse or modify it, enhancing trust in the blockchain's immutability.
User Experience
: Transaction status greatly impacts the user experience of blockchain applications. Delays or failures in transaction processing can frustrate users and hinder the adoption of decentralized applications (dApps).Guidance for Users
1.
Monitor Transaction Status
: Utilize blockchain explorers or wallet interfaces to track the status of your transactions. This helps you stay informed about the progress of your transactions and take necessary actions if they encounter issues.2.
Set Optimal Fees
: When initiating transactions, ensure that you set appropriate transaction fees to incentivize miners or validators to prioritize your transaction. Low fees may result in delays or the rejection of your transaction by the network.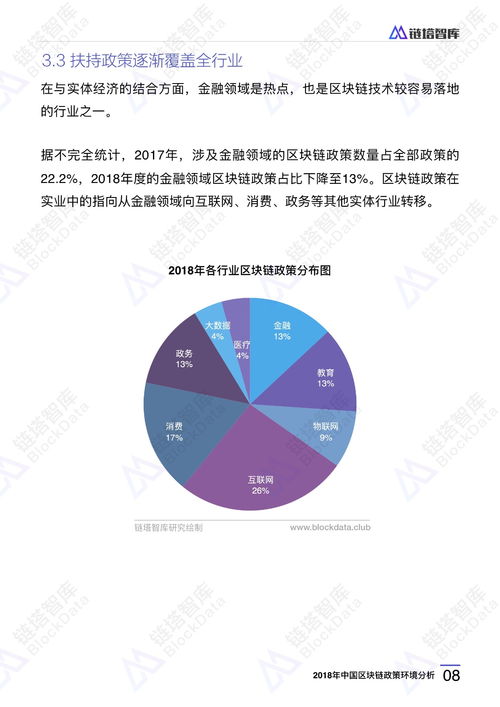
3.
Stay Informed
: Stay updated with developments in blockchain technology, especially regarding upgrades or changes in transaction processing mechanisms. This enables you to adapt your transaction strategies accordingly and optimize your experience.In conclusion, transaction status in blockchain networks reflects the current state of transactions and plays a crucial role in determining their security, reliability, and efficiency. Understanding the implications of different transaction statuses empowers users to navigate the blockchain ecosystem effectively and make informed decisions regarding their transactions.
版权声明
本文仅代表作者观点,不代表百度立场。
本文系作者授权百度百家发表,未经许可,不得转载。

















评论