Title: Understanding Bitcoin: A Comprehensive Overview
Bitcoin has garnered significant attention since its inception in 2009, revolutionizing the financial landscape and challenging traditional notions of currency. This presentation aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Bitcoin, covering its underlying technology, its impact on finance, its advantages, risks, and future prospects.
Introduction to Bitcoin
Bitcoin, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, was introduced by an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a peertopeer network, utilizing blockchain technology to facilitate transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
How Bitcoin Works
Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain. The blockchain is a decentralized and distributed database maintained by a network of computers, known as nodes. Transactions are grouped into blocks and added to the blockchain through a process called mining, where miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and secure the network.
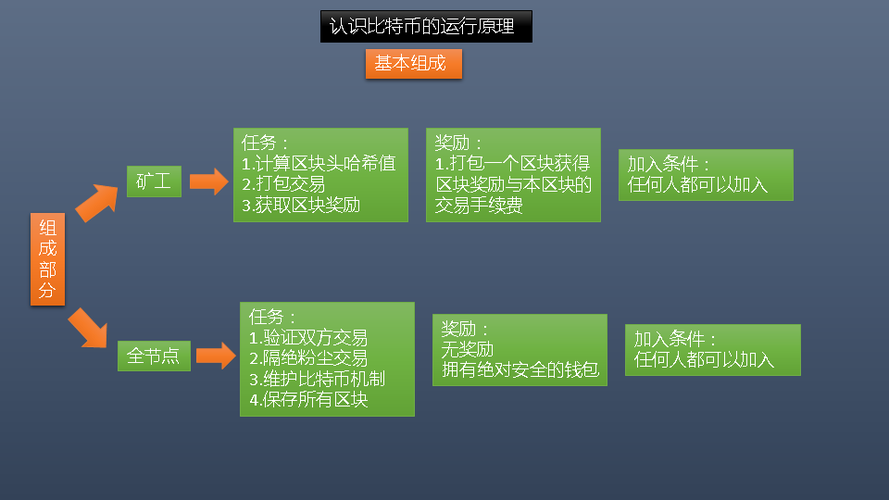
Key Features of Bitcoin
1.
Decentralization
: Bitcoin operates without a central authority, making it resistant to censorship and manipulation.2.
Limited Supply
: There will only ever be 21 million bitcoins, making it a deflationary asset.3.
Pseudonymity
: While transactions are recorded on the blockchain, users' identities are not directly tied to their Bitcoin addresses.4.
Transparency
: All transactions are publicly recorded on the blockchain, allowing anyone to verify them.Advantages of Bitcoin
1.
Borderless Transactions
: Bitcoin enables seamless crossborder transactions without the need for currency conversion or intermediaries.2.
Lower Transaction Fees
: Compared to traditional banking systems, Bitcoin transactions typically have lower fees, especially for international transfers.3.
Financial Inclusion
: Bitcoin provides access to financial services for the unbanked and underbanked populations, particularly in regions with limited banking infrastructure.4.
Store of Value
: Many view Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation and store of value similar to gold.Risks and Challenges
1.
Volatility
: Bitcoin prices are highly volatile, posing risks for investors and merchants.2.
Regulatory Uncertainty
: Regulatory scrutiny varies across jurisdictions, leading to uncertainty regarding the legal status of Bitcoin.3.
Security Concerns
: While the blockchain itself is secure, individual wallets and exchanges are susceptible to hacking and theft.4.
Environmental Impact
: Bitcoin mining consumes a significant amount of energy, raising concerns about its environmental sustainability.Future Outlook
Despite the challenges, Bitcoin continues to gain adoption as a legitimate asset class and means of payment. Institutional investors are increasingly entering the market, and major companies are accepting Bitcoin as payment. Moreover, ongoing developments in scalability and privacy solutions aim to address some of Bitcoin's limitations.
Conclusion
Bitcoin represents a groundbreaking innovation in the realm of finance, offering decentralization, security, and financial sovereignty to its users. While it faces challenges and uncertainties, its potential to reshape the global financial system cannot be overlooked. Understanding Bitcoin is not just about grasping a new technology but also about embracing a paradigm shift in the way we perceive and interact with money.
版权声明
本文仅代表作者观点,不代表百度立场。
本文系作者授权百度百家发表,未经许可,不得转载。

















评论